Template And Coding Strand
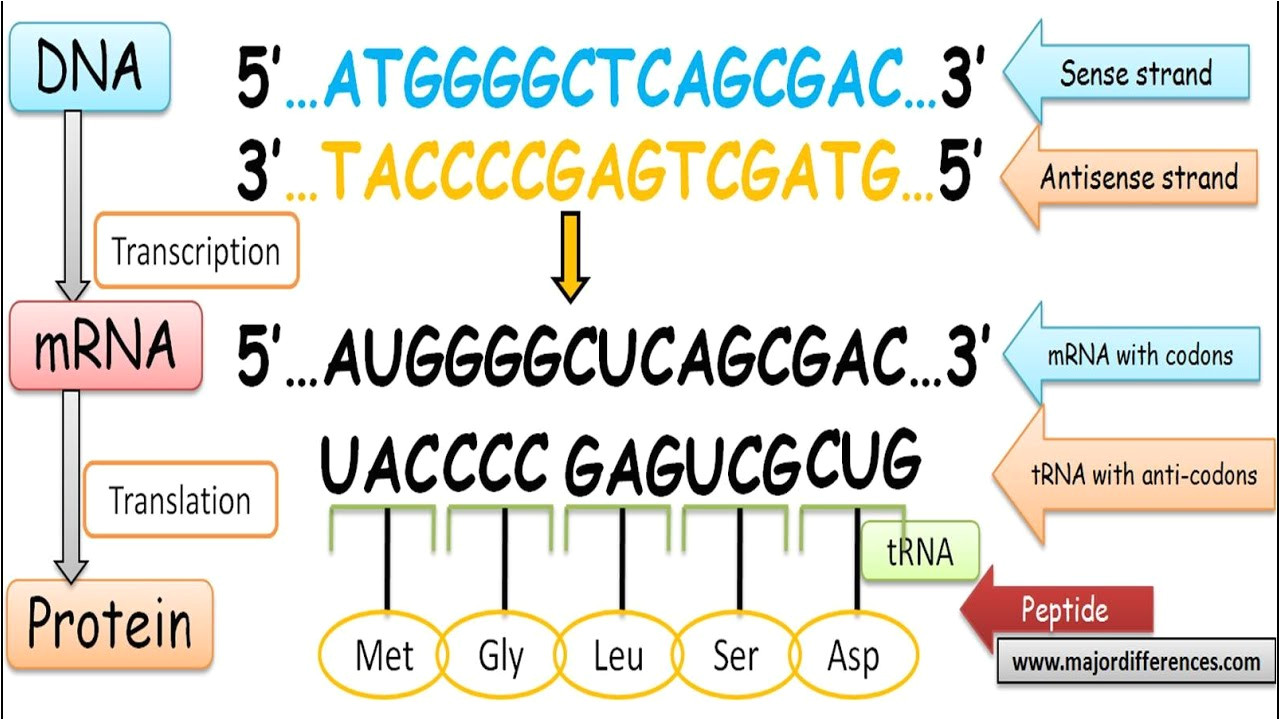
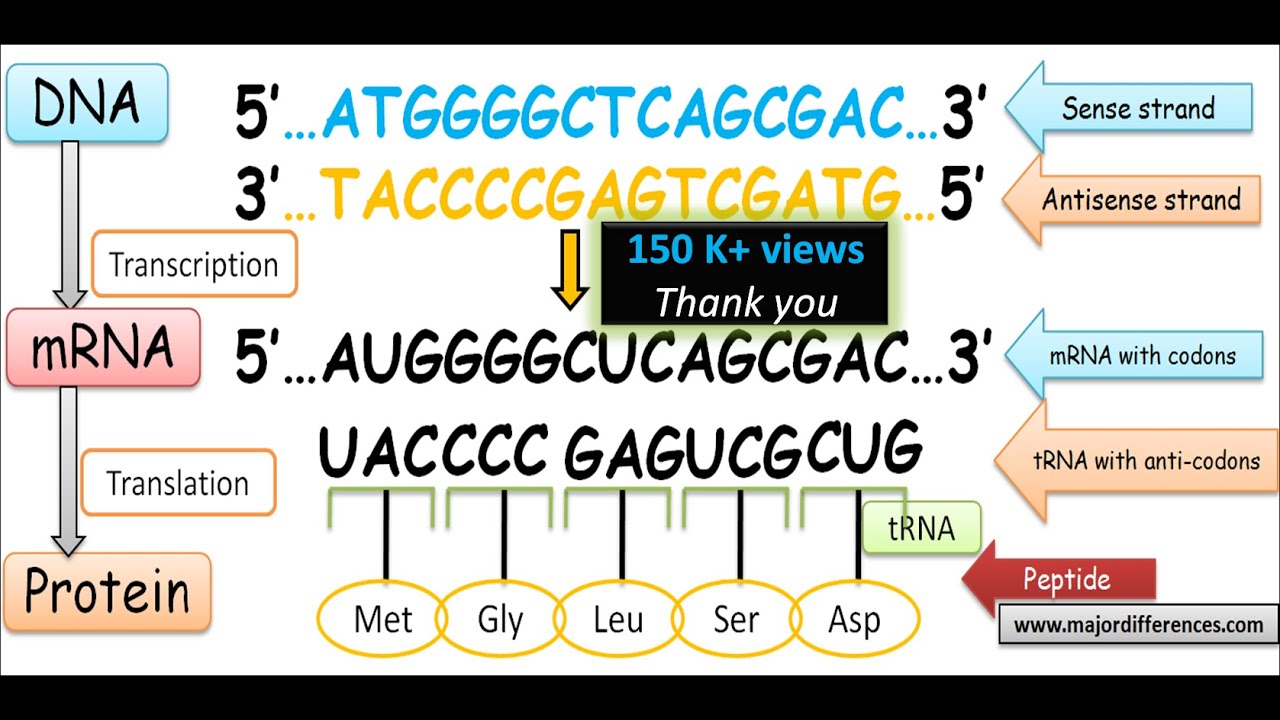
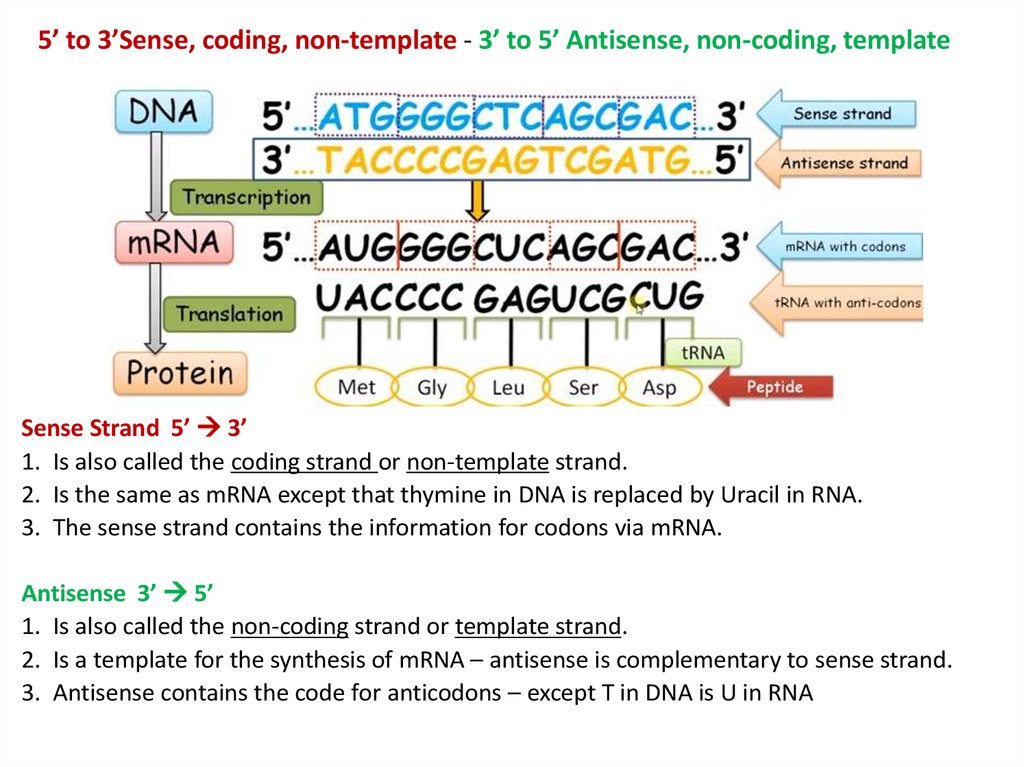
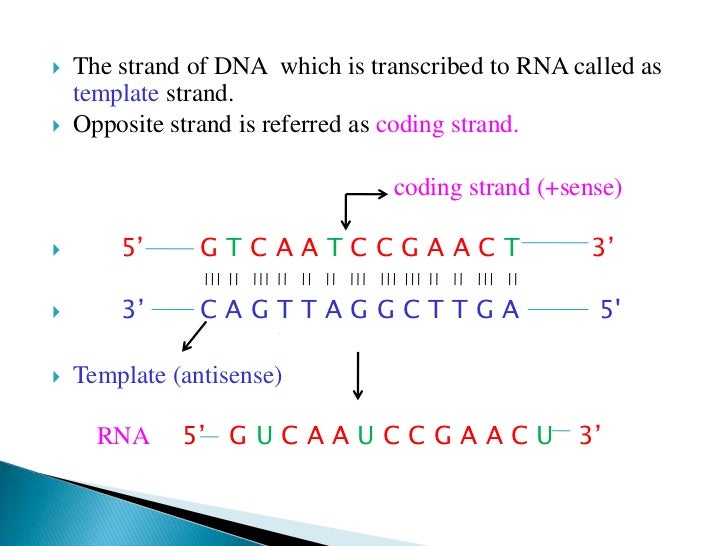
Template And Coding Strand - The coding strand determines the correct nucleotide sequence of mrna. Most codons specify an amino acid three. Here are some features of codons: Web in transcription, a region of dna opens up. Web codons cells decode mrnas by reading their nucleotides in groups of three, called codons. One strand, the template strand, serves as a template for synthesis of a complementary rna transcript. When referring to dna transcription, the coding strand (or informational strand) is the dna strand. Web position of the template and coding strands during transcription. Here are some features of codons: Web in transcription, a region of dna opens up. When referring to dna transcription, the coding strand (or informational strand) is the dna strand. Most codons specify an amino acid three. One strand, the template strand, serves as a template for synthesis of a complementary rna transcript. Most codons specify an amino acid three. Here are some features of codons: One strand, the template strand, serves as a template for synthesis of a complementary rna transcript. The coding strand determines the correct nucleotide sequence of mrna. Web position of the template and coding strands during transcription. One strand, the template strand, serves as a template for synthesis of a complementary rna transcript. Most codons specify an amino acid three. The coding strand determines the correct nucleotide sequence of mrna. Web position of the template and coding strands during transcription. Here are some features of codons: Web in transcription, a region of dna opens up. Web codons cells decode mrnas by reading their nucleotides in groups of three, called codons. When referring to dna transcription, the coding strand (or informational strand) is the dna strand. The coding strand determines the correct nucleotide sequence of mrna. Most codons specify an amino acid three. One strand, the template strand, serves as a template for synthesis of a complementary rna transcript. Here are some features of codons: When referring to dna transcription, the coding strand (or informational strand) is the dna strand. Web codons cells decode mrnas by reading their nucleotides in groups of three, called codons. Web position of the template and coding strands. Web codons cells decode mrnas by reading their nucleotides in groups of three, called codons. When referring to dna transcription, the coding strand (or informational strand) is the dna strand. The coding strand determines the correct nucleotide sequence of mrna. Web position of the template and coding strands during transcription. One strand, the template strand, serves as a template for. The coding strand determines the correct nucleotide sequence of mrna. Most codons specify an amino acid three. When referring to dna transcription, the coding strand (or informational strand) is the dna strand. Web codons cells decode mrnas by reading their nucleotides in groups of three, called codons. Web position of the template and coding strands during transcription. Web position of the template and coding strands during transcription. Most codons specify an amino acid three. When referring to dna transcription, the coding strand (or informational strand) is the dna strand. Web in transcription, a region of dna opens up. The coding strand determines the correct nucleotide sequence of mrna. The coding strand determines the correct nucleotide sequence of mrna. When referring to dna transcription, the coding strand (or informational strand) is the dna strand. Web in transcription, a region of dna opens up. Web position of the template and coding strands during transcription. Web codons cells decode mrnas by reading their nucleotides in groups of three, called codons. The coding strand determines the correct nucleotide sequence of mrna. When referring to dna transcription, the coding strand (or informational strand) is the dna strand. Web codons cells decode mrnas by reading their nucleotides in groups of three, called codons. Here are some features of codons: Web in transcription, a region of dna opens up. Web position of the template and coding strands during transcription. Most codons specify an amino acid three. Web in transcription, a region of dna opens up. The coding strand determines the correct nucleotide sequence of mrna. Web codons cells decode mrnas by reading their nucleotides in groups of three, called codons. One strand, the template strand, serves as a template for synthesis of a complementary rna transcript. When referring to dna transcription, the coding strand (or informational strand) is the dna strand. Here are some features of codons: Here are some features of codons: Web in transcription, a region of dna opens up. The coding strand determines the correct nucleotide sequence of mrna. Web codons cells decode mrnas by reading their nucleotides in groups of three, called codons. One strand, the template strand, serves as a template for synthesis of a complementary rna transcript. Most codons specify an amino acid three.Difference Between Template and Coding Strand williamsonga.us
IMP Coding (Sense) vs Template (AntiSense) Strands Biology activity
Coding Strand of DNA bartleby
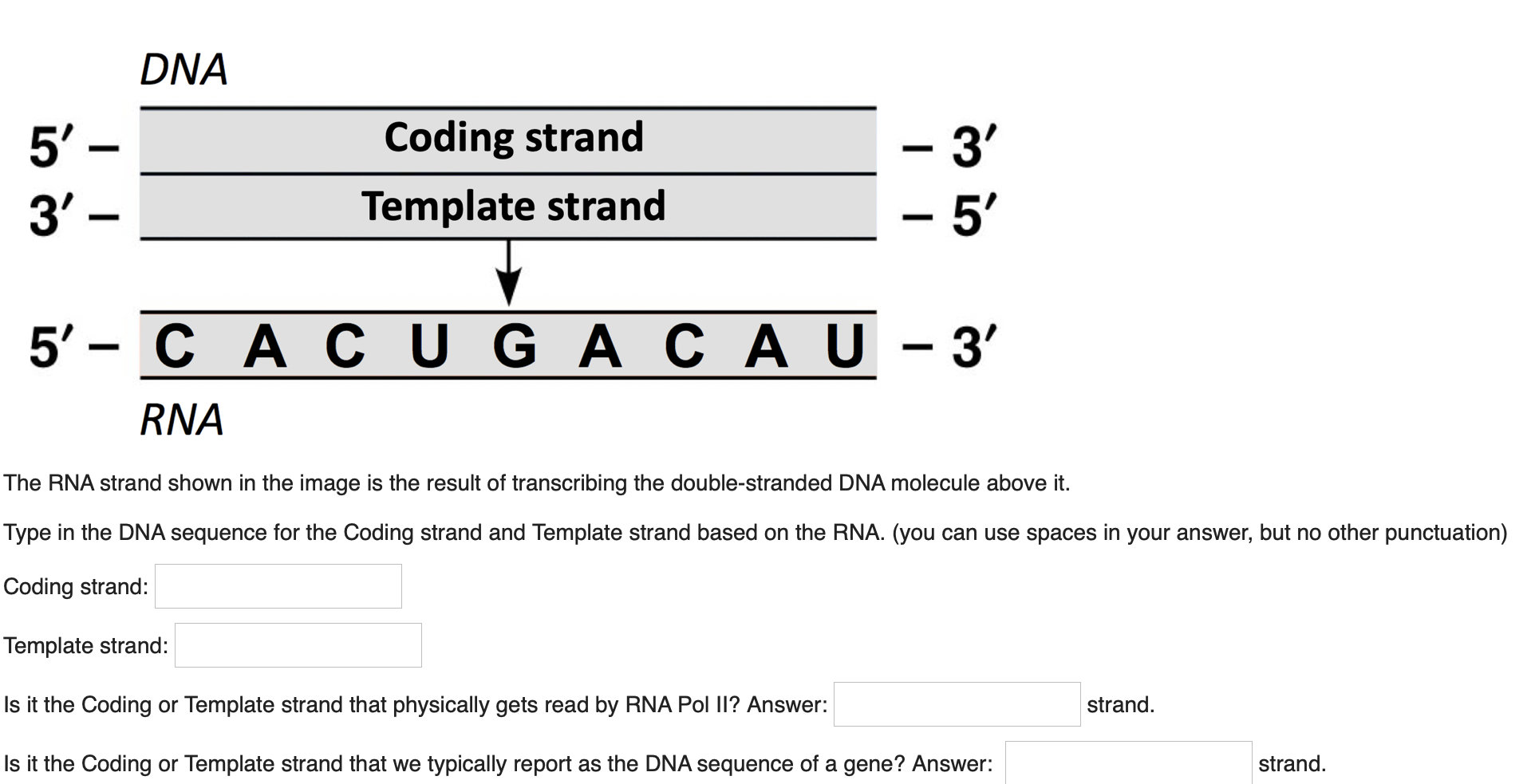
The coding strand of DNA is 5'AATTCAAATTAGG3'
Difference Between Template and Coding Strand
Template vs. Nontemplate (Noncoding vs. Coding strand of DNA) YouTube
Difference between Sense Strand and Antisense Strand of DNA YouTube
Solved DNA 5' 3' Coding strand Template strand 3' 5'
Transcription and Translation and the Code online presentation
Transcription
When Referring To Dna Transcription, The Coding Strand (Or Informational Strand) Is The Dna Strand.
Web Position Of The Template And Coding Strands During Transcription.
Related Post: